Albuterol sulfate
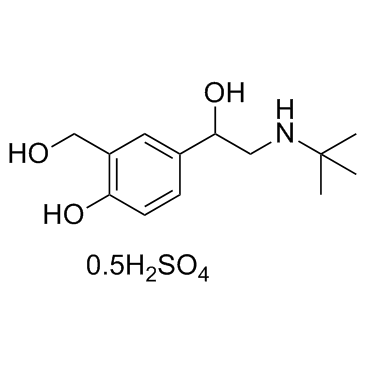
Albuterol sulfate structure
|
Common Name | Albuterol sulfate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 51022-70-9 | Molecular Weight | 288.14 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 419.2ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C13H22NO5S0.5 | Melting Point | 180 °C | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 250 °C | |
|
Optimizing the primary particle size distributions of pressurized metered dose inhalers by using inkjet spray drying for targeting desired regions of the lungs.
Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 41(2) , 279-91, (2015) Conventional suspension pressurized metered dose inhalers (pMDIs) suffer not only from delivering small amounts of a drug to the lungs, but also the inhaled dose scatters all over the lung regions. This results in much less of the desired dose being delivered... |
|
|
Lipophilicity of amine neurotransmitter precursors, metabolites and related drugs estimated on various TLC plates.
J. Chromatogr. Sci. 52(9) , 1095-103, (2014) The retention behavior for a series of amine neurotransmitters, their precursors, metabolites and structurally related drugs has been investigated in reversed-phase thin-layer chromatography using RP-18, RP-8, RP-2, CN and Diol stationary phases and mixtures ... |
|
|
Salmeterol's extreme β2 selectivity is due to residues in both extracellular loops and transmembrane domains.
Mol. Pharmacol. 87(1) , 103-20, (2015) Salmeterol is a long-acting β2-agonist, widely used as an inhaled treatment of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. It has very high β2-affinity (log KD -8.95) and is very selective for the β2-adrenoceptor (1000-fold selectivity over the β1-adren... |
|
|
Nebulization of active pharmaceutical ingredients with the eFlow(®) rapid: impact of formulation variables on aerodynamic characteristics.
J. Pharm. Sci. 103(8) , 2585-9, (2014) Nebulization of active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) solutions is a well-established means to achieve pulmonary drug deposition. The current study identified the impact of formulation variables on the aerosolization performance of the eFlow(®) rapid with sp... |
|
|
Plp1 gene duplication inhibits airway responsiveness and induces lung inflammation.
Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 30 , 22-31, (2015) Mice with Plp1 gene duplication model the most common form of Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease (PMD), a CNS disease in which patients may suffer respiratory complications. We hypothesized that affected mice would lack airway responsiveness compared to wild-type a... |
|
|
Uptake and effects of a mixture of widely used therapeutic drugs in Eruca sativa L. and Zea mays L. plants.
Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 108 , 52-7, (2014) Pharmaceutically active compounds (PACs) are continuously dispersed into the environment due to human and veterinary use, giving rise to their potential accumulation in edible plants. In this study, Eruca sativa L. and Zea mays L. were selected to determine t... |
|
|
Liquid crystalline phase as a probe for crystal engineering of lactose: carrier for pulmonary drug delivery.
Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 68 , 43-50, (2015) The current work was undertaken to assess suitability of liquid crystalline phase for engineering of lactose crystals and their utility as a carrier in dry powder inhalation formulations. Saturated lactose solution was poured in molten glyceryl monooleate whi... |
|
|
Calcium release-activated calcium (CRAC) channels mediate the β(2)-adrenergic regulation of Na,K-ATPase.
FEBS Lett. 588(24) , 4686-93, (2014) β2-Adrenergic agonists have been shown to regulate Na,K-ATPase in the alveolar epithelium by recruiting Na,K-ATPase-containing vesicles to the plasma membrane of alveolar epithelial cells (AEC). Here, we provide evidence that β2-agonists induce store-operated... |
|
|
Factors influencing aerodynamic particle size distribution of suspension pressurized metered dose inhalers.
AAPS PharmSciTech 16(1) , 192-201, (2015) Pressurized metered dose inhalers (pMDIs) are frequently used for the treatment of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. The aerodynamic particle size distribution (APSD) of the residual particles delivered from a pMDI plays a key role in determin... |
|
|
Modeling and Understanding Combination pMDI Formulations with Both Dissolved and Suspended Drugs.
Mol. Pharm. 12 , 3455-67, (2015) A simulation model has been established to predict the residual aerodynamic particle size distribution (APSD) of dual-component pressurized metered dose inhalers (pMDIs). More specifically, this model estimates the APSD of pMDI formulations containing dissolv... |