| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
 |
4-aminosalicylic acid
CAS:65-49-6 |
|
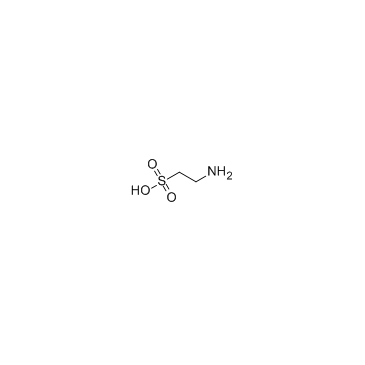 |
Taurine
CAS:107-35-7 |
|
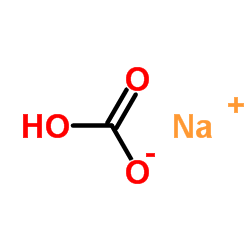 |
SodiuM bicarbonate
CAS:144-55-8 |
|
 |
HEPES
CAS:7365-45-9 |
|
 |
SODIUM CHLORIDE-35 CL
CAS:20510-55-8 |
|
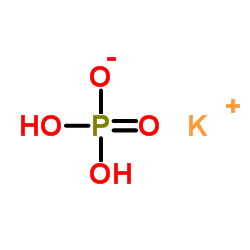 |
Monopotassium phosphate
CAS:7778-77-0 |
|
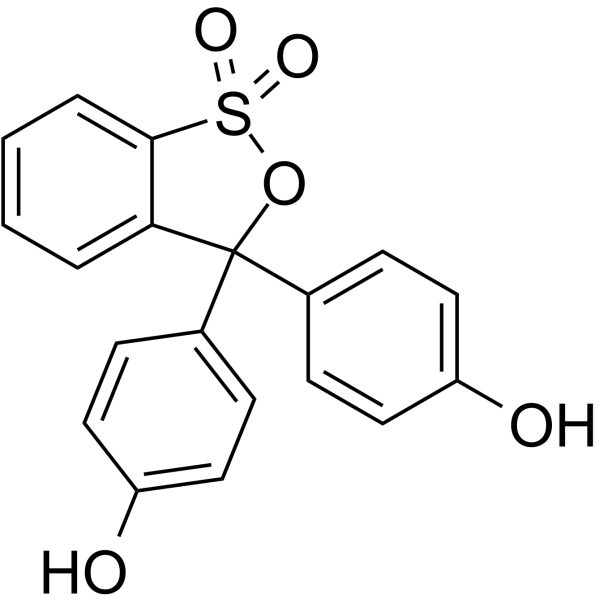 |
Phenol red
CAS:143-74-8 |
|
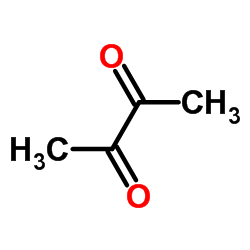 |
butane-2,3-dione
CAS:431-03-8 |