| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Ethanol
CAS:64-17-5 |
|
 |
Methanol
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
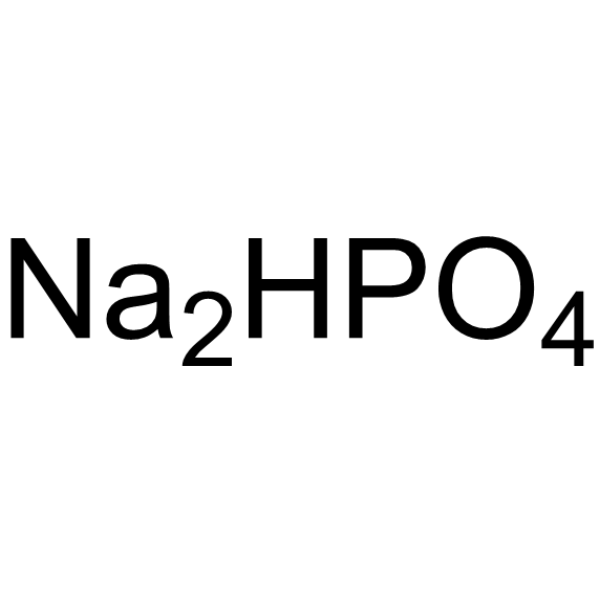 |
Disodium hydrogenorthophosphate
CAS:7558-79-4 |
|
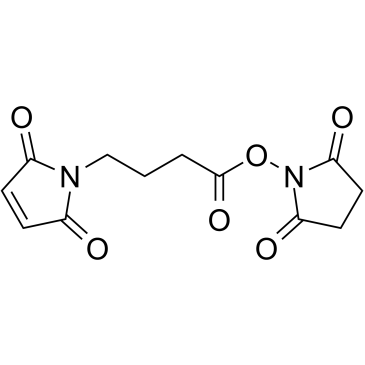 |
gmbs
CAS:80307-12-6 |
|
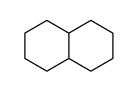 |
Decahydronaphthalene
CAS:91-17-8 |
|
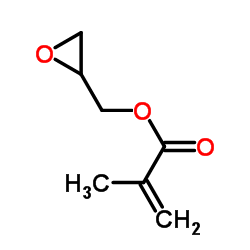 |
Glycidyl methacrylate
CAS:106-91-2 |
|
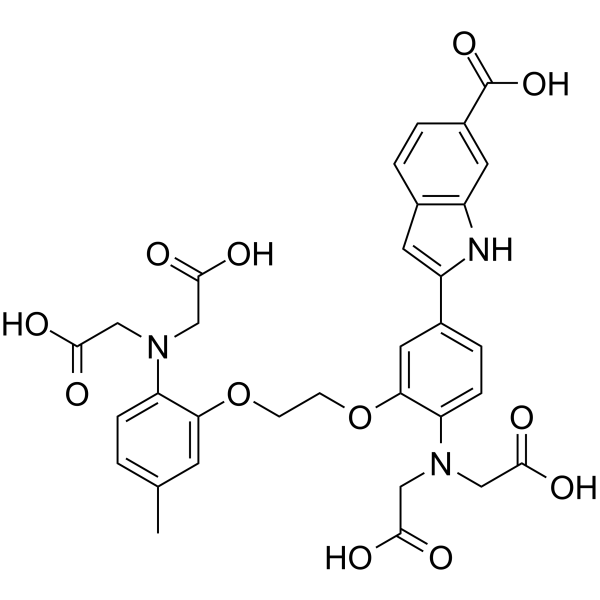 |
Indo 1
CAS:96314-96-4 |
|
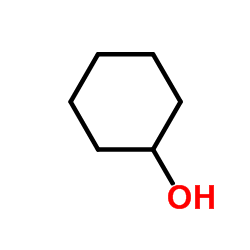 |
Cyclohexanol
CAS:108-93-0 |
|
 |
DMPA
CAS:24650-42-8 |
|
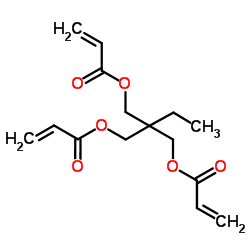 |
Trimethylolpropane triacrylate
CAS:15625-89-5 |