| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Ethanol
CAS:64-17-5 |
|
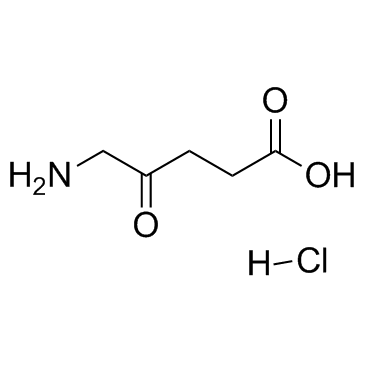 |
5-Aminolevulinic acid hydrochloride
CAS:5451-09-2 |
|
 |
Tamoxifen
CAS:10540-29-1 |
|
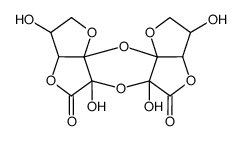 |
Empirical Formula(Hill Notation)
CAS:72691-25-9 |