| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
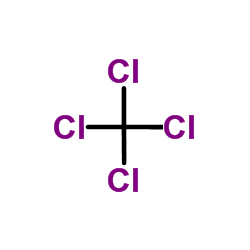 |
Carbon tetrachloride
CAS:56-23-5 |
|
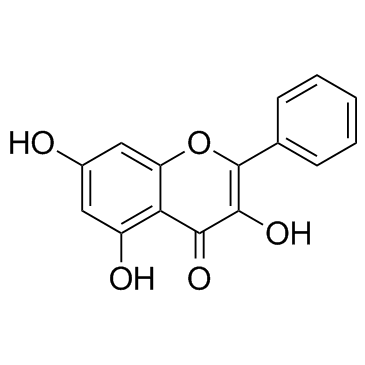 |
Galangin
CAS:548-83-4 |