| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
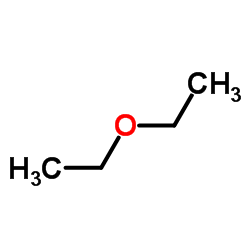 |
Diethyl ether
CAS:60-29-7 |
|
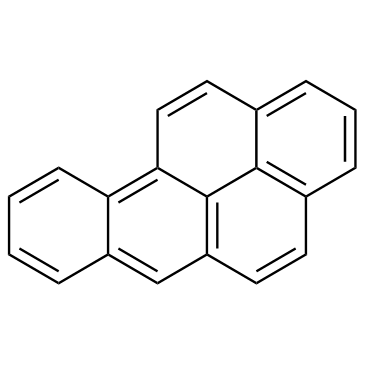 |
Benzo(a)pyrene
CAS:50-32-8 |
|
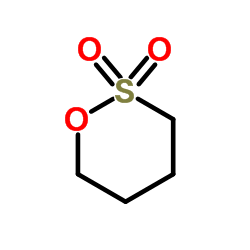 |
1,4-Butane sultone
CAS:1633-83-6 |