| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
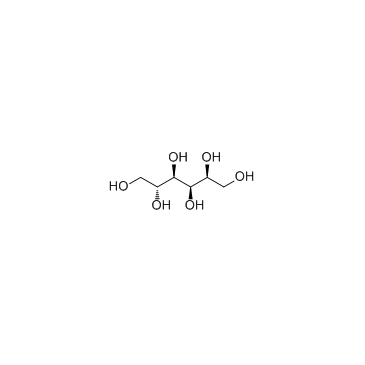 |
Sorbitol
CAS:50-70-4 |
|
 |
Calcium chloride
CAS:10043-52-4 |
|
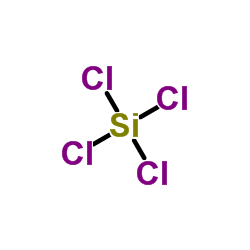 |
Tetrachlorosilane
CAS:10026-04-7 |
|
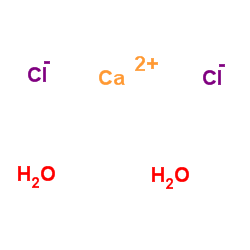 |
calcium chloride dihydrate
CAS:10035-04-8 |
|
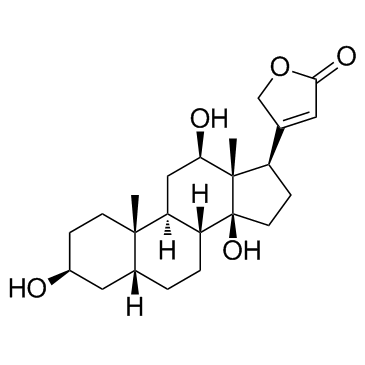 |
Digoxigenin
CAS:1672-46-4 |