| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
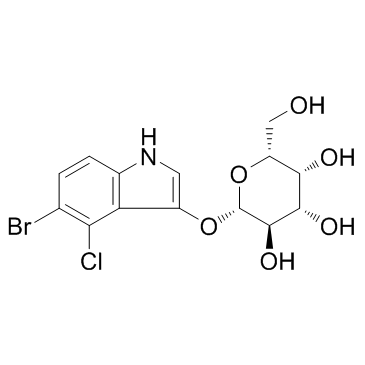 |
5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl β-D-galactoside
CAS:7240-90-6 |
|
 |
Erythromycin
CAS:114-07-8 |
|
 |
Griseofulvin
CAS:126-07-8 |