| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
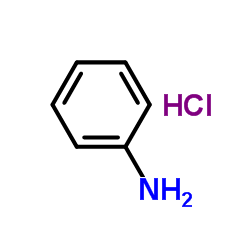 |
Anilinium chloride
CAS:142-04-1 |
|
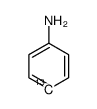 |
<4-13C>Aniline-4-13C
CAS:55147-71-2 |
|
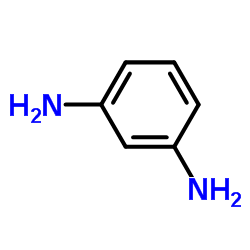 |
m-Phenylenediamine
CAS:108-45-2 |
|
 |
Aniline
CAS:62-53-3 |
|
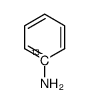 |
Anilin-<1-13C>
CAS:18960-62-8 |