PcpA, which is involved in the degradation of pentachlorophenol in Sphingomonas chlorophenolica ATCC39723, is a novel type of ring-cleavage dioxygenase.
Y Ohtsubo, K Miyauchi, K Kanda, T Hatta, H Kiyohara, T Senda, Y Nagata, Y Mitsui, M Takagi
Index: FEBS Lett. 459(3) , 395-8, (1999)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The pentachlorophenol (PCP) mineralizing bacterium Sphingomonas chlorophenolica ATCC39723 degrades PCP via 2,6-dichlorohydroquinone (2,6-DCHQ). The pathway converting PCP to 2,6-DCHQ has been established previously; however, the pathway beyond 2,6-DCHQ is not clear, although it has been suggested that a PcpA plays a role in 2, 6-DCHQ conversion. In this study, PcpA expressed in Escherichia coli was purified to homogeneity and shown to have novel ring-cleavage dioxygenase activity in conjunction with hydroquinone derivatives, and converting 2,6-DCHQ to 2-chloromaleylacetate.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
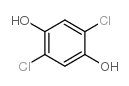 |
2,5-DICHLOROHYDROQUINONE
CAS:824-69-1 |
C6H4Cl2O2 |
|
Sequence analysis of a gene cluster involved in metabolism o...
1995-04-01 [Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 61(4) , 1279-89, (1995)] |
|
Degradation of the chlorinated phenoxyacetate herbicides 2,4...
1990-05-01 [Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 56(5) , 1357-62, (1990)] |
|
Cloning and sequencing of a 2,5-dichloro-2,5-cyclohexadiene-...
1994-06-01 [J. Bacteriol. 176(11) , 3117-25, (1994)] |
|
Cloning and sequencing of a 2,5-dichlorohydroquinone reducti...
1998-03-01 [J. Bacteriol. 180(6) , 1354-9, (1998)] |
|
Copper-mediated DNA damage by metabolites of p-dichlorobenze...
1996-12-01 [Carcinogenesis 17(12) , 2733-9, (1996)] |