2,5-DICHLOROHYDROQUINONE
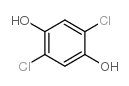
2,5-DICHLOROHYDROQUINONE structure
|
Common Name | 2,5-DICHLOROHYDROQUINONE | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 824-69-1 | Molecular Weight | 179.00100 | |
| Density | 1.624g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 274ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H4Cl2O2 | Melting Point | 168-171 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 119.5ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS05 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
| Name | 2,5-dichlorohydroquinone |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 1.624g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 274ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 168-171 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C6H4Cl2O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 179.00100 |
| Flash Point | 119.5ºC |
| Exact Mass | 177.95900 |
| PSA | 40.46000 |
| LogP | 2.40460 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.642 |
| InChIKey | AYNPIRVEWMUJDE-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | Oc1cc(Cl)c(O)cc1Cl |
| Symbol |

GHS05 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H314 |
| Precautionary Statements | P280-P305 + P351 + P338-P310 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;full-face particle respirator type N100 (US);Gloves;respirator cartridge type N100 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter;type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | C:Corrosive; |
| Risk Phrases | R34 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S27-S36/37/39-S45 |
| RIDADR | UN 3261 8/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| HS Code | 2908199090 |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 6 | |
| HS Code | 2908199090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | HS: 2908199090. derivatives of polyphenols or phenol-alcohols containing only halogen substituents and their salts. VAT:17.0%. tax rebate rate:9.0%. supervision conditions:None. MFN tariff:5.5%. general tariff:30.0% |
|
Sequence analysis of a gene cluster involved in metabolism of 2,4,5-trichlorophenoxyacetic acid by Burkholderia cepacia AC1100.
Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 61(4) , 1279-89, (1995) Burkholderia cepacia AC1100 utilizes 2,4,5-trichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4,5-T) as a sole source of carbon and energy. PT88 is a chromosomal deletion mutant of B. cepacia AC1100 and is unable to grow... |
|
|
Degradation of the chlorinated phenoxyacetate herbicides 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid and 2,4,5-trichlorophenoxyacetic acid by pure and mixed bacterial cultures.
Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 56(5) , 1357-62, (1990) Combined cell suspensions of the 2,4,5-trichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4,5-T)-metabolizing organism Pseudomonas cepacia AC1100, and the 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D)-metabolizing organism Alca... |
|
|
PcpA, which is involved in the degradation of pentachlorophenol in Sphingomonas chlorophenolica ATCC39723, is a novel type of ring-cleavage dioxygenase.
FEBS Lett. 459(3) , 395-8, (1999) The pentachlorophenol (PCP) mineralizing bacterium Sphingomonas chlorophenolica ATCC39723 degrades PCP via 2,6-dichlorohydroquinone (2,6-DCHQ). The pathway converting PCP to 2,6-DCHQ has been establis... |
| 1,4-Benzenediol,2,5-dichloro |
| EINECS 212-533-8 |
| 2,5-Dichloro-p-hydroquinone |
| Hydroquinone,2,5-dichloro |
| 2,4-DIFLUORO THIOANISOLE |
| 2,5-dichloro-1,4-dihydroxybenzene |
| 2,5-Dichlorohydroquinone |
| 2,5-DCHQ |
| 2,5-dichloro-1,4-hydroquinone |
| 2,5-Dichloro-1,4-benzenediol |
| MFCD00041749 |
| 2,5-dichlorobenzene-1,4-diol |
| 2,5-dichloro-4-hydroxyphenol |
| 2,5-Dichloro-p-benzohydroquinone |
| 1,4-dichloro-2,5-dihydroxybenzene |
| 2,5-dichlorohydroquinol |
 CAS#:695-99-8
CAS#:695-99-8 CAS#:615-93-0
CAS#:615-93-0 CAS#:1073-95-6
CAS#:1073-95-6 CAS#:123-31-9
CAS#:123-31-9 CAS#:150-13-0
CAS#:150-13-0 CAS#:92-85-3
CAS#:92-85-3 CAS#:563-43-9
CAS#:563-43-9 CAS#:50392-39-7
CAS#:50392-39-7 CAS#:106-51-4
CAS#:106-51-4 CAS#:63335-14-8
CAS#:63335-14-8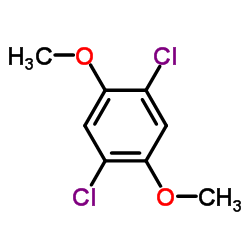 CAS#:2675-77-6
CAS#:2675-77-6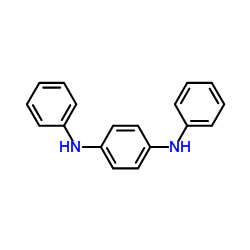 CAS#:74-31-7
CAS#:74-31-7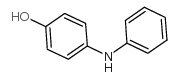 CAS#:122-37-2
CAS#:122-37-2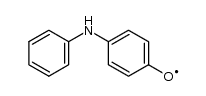 CAS#:34865-89-9
CAS#:34865-89-9 CAS#:122-39-4
CAS#:122-39-4