| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Acetonitrile
CAS:75-05-8 |
|
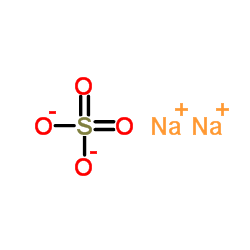 |
sodium sulfate
CAS:7757-82-6 |
|
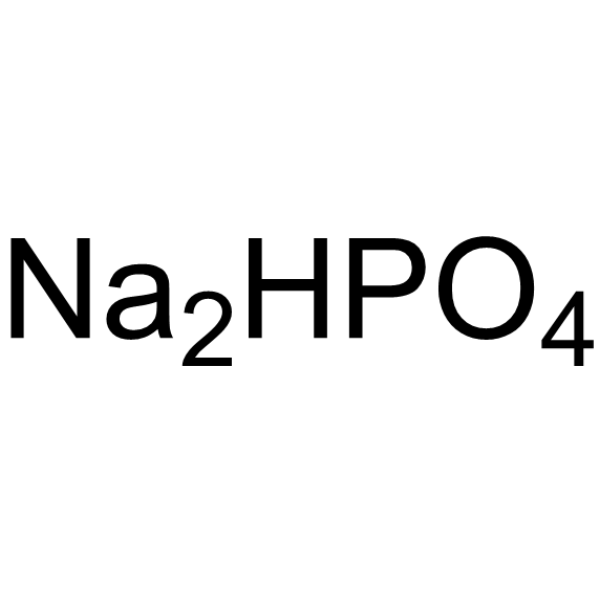 |
Disodium hydrogenorthophosphate
CAS:7558-79-4 |
|
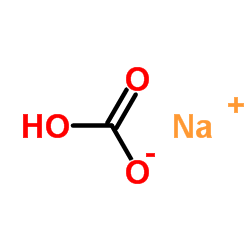 |
SodiuM bicarbonate
CAS:144-55-8 |
|
 |
sodium dihydrogenphosphate
CAS:7558-80-7 |
|
 |
Ammonium iodide
CAS:12027-06-4 |
|
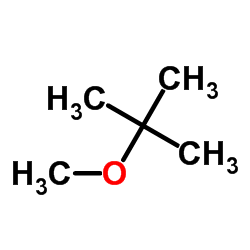 |
Methyl tert-butyl ether
CAS:1634-04-4 |
|
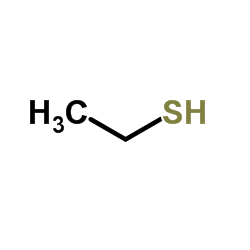 |
Ethanethiol
CAS:75-08-1 |
|
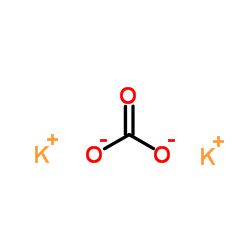 |
Potassium carbonate
CAS:584-08-7 |
|
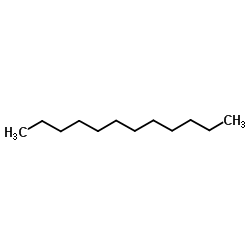 |
Dodecane
CAS:112-40-3 |