| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
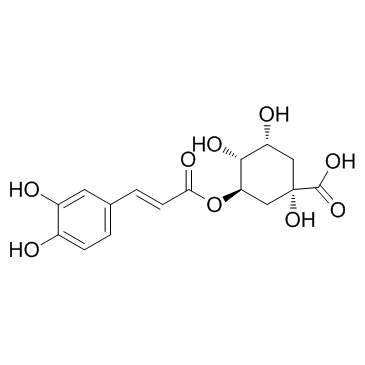 |
Chlorogenic acid
CAS:327-97-9 |
|
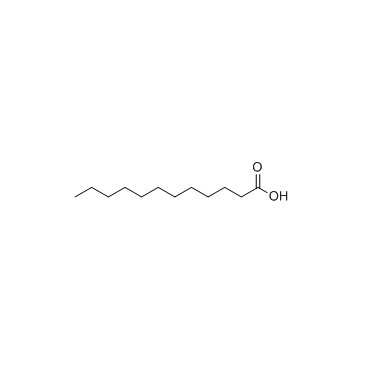 |
Lauric acid
CAS:143-07-7 |
|
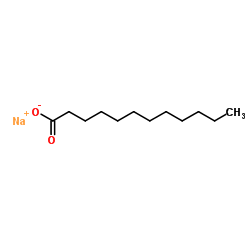 |
Sodium laurate
CAS:629-25-4 |
|
 |
L-Histidine Decarboxylase
CAS:9024-61-7 |