| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
sodium dodecyl sulfate
CAS:151-21-3 |
|
 |
acetic acid
CAS:64-19-7 |
|
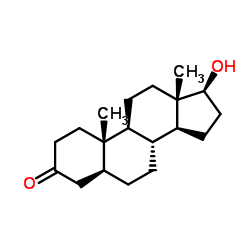 |
Stanolone
CAS:521-18-6 |
|
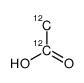 |
acetic acid
CAS:1173022-32-6 |
|
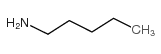 |
Amylamine
CAS:110-58-7 |
|
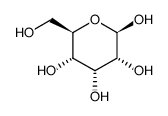 |
Beta-D-allose
CAS:7283-09-2 |