| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Formaldehyde
CAS:50-00-0 |
|
 |
Dimethyl sulfoxide
CAS:67-68-5 |
|
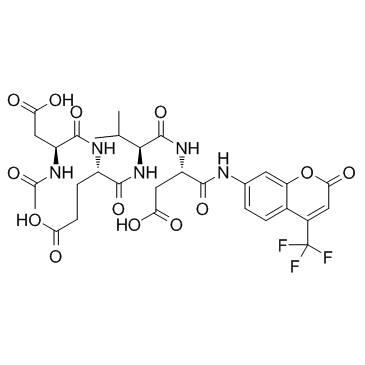 |
Ac-Asp-Glu-Val-Asp-AFC
CAS:201608-14-2 |
|
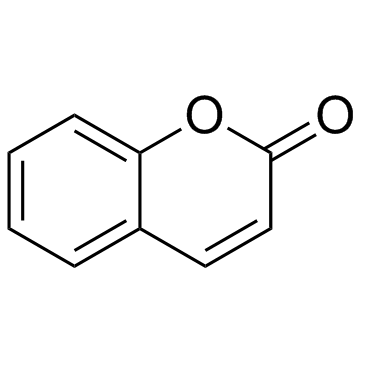 |
Coumarin
CAS:91-64-5 |
|
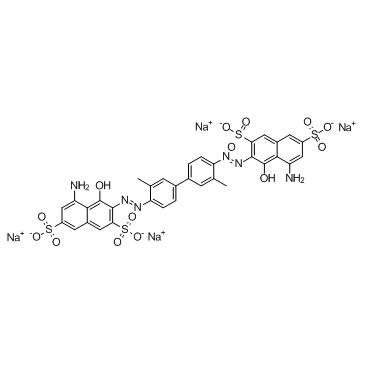 |
Direct Blue 14
CAS:72-57-1 |
|
 |
H2DCFDA
CAS:4091-99-0 |
|
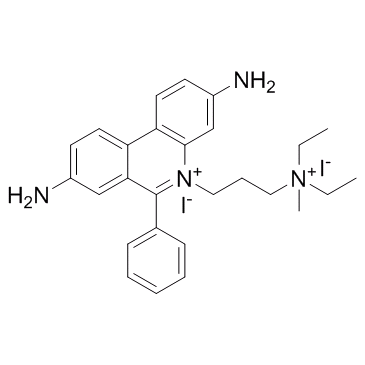 |
Propidium Iodide
CAS:25535-16-4 |
|
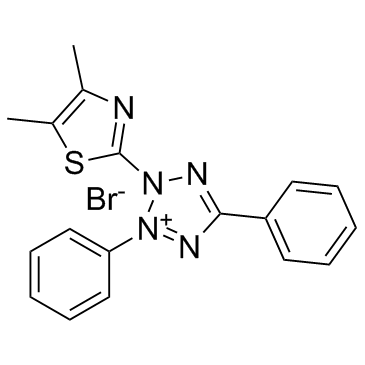 |
Thiazolyl Blue
CAS:298-93-1 |
|
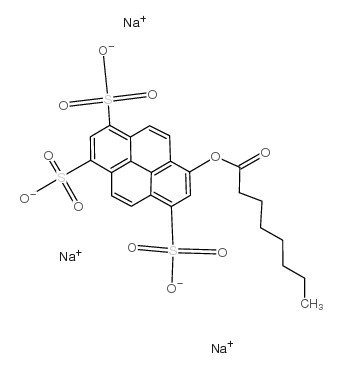 |
8-Octanoyloxypyrene-1,3,6-trisulfonic acid trisodium salt
CAS:115787-84-3 |