| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Dichloromethane
CAS:75-09-2 |
|
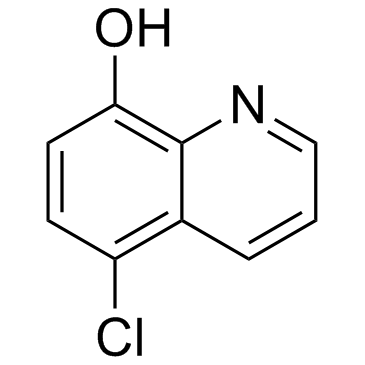 |
5-Chloro-8-hydroxyquinoline
CAS:130-16-5 |