| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
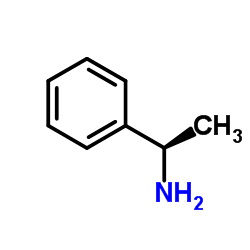 |
L-1-Phenylethylamine
CAS:2627-86-3 |
|
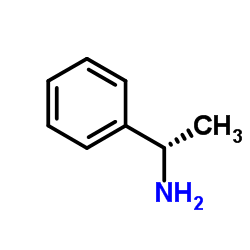 |
(R)-(+)-1-Phenylethylamine
CAS:3886-69-9 |
|
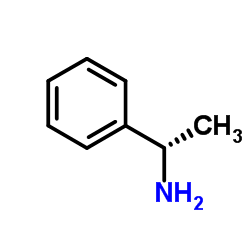 |
1-Phenylethanamine
CAS:618-36-0 |