Recurrent COLQ mutation in congenital myasthenic syndrome.
Alev Guven, Mehmet Demirci, Banu Anlar
Index: Pediatr. Neurol. 46(4) , 253-6, (2012)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Congenital myasthenic syndromes comprise clinically and genetically heterogeneous disorders resulting from presynaptic, synaptic, or postsynaptic defects. Mutations in the COLQ gene result in acetylcholinesterase deficiency and cause a rare, autosomal recessive synaptic form of congenital myasthenic syndrome, with variable age of onset and clinical severity. We present four unrelated patients with a homozygous W148X mutation in the COLQ gene. Signs began at birth in all, but subsequent severity ranged from independent ambulation to wheelchair use during childhood. Treatment was partly effective; one patient was asymptomatic with 3,4-diaminopyridine treatment. These cases illustrate the clinical features and treatment results associated with this particular genotype, which appears to be relatively frequent among Turkish patients with congenital myasthenic syndrome.Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
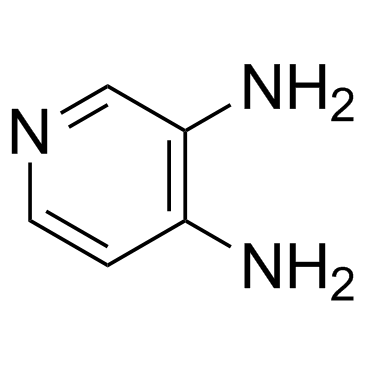 |
3,4-Diaminopyridine
CAS:54-96-6 |
C5H7N3 |
|
Novel HPLC--Fluorescence methodology for the determination o...
2015-11-15 [Food Chem. 187 , 159-65, (2015)] |
|
Ectopic uterine tissue as a chronic pain generator.
2012-12-06 [Neuroscience 225 , 269-82, (2012)] |
|
3-D-QSAR and docking studies on the neuronal choline transpo...
2010-08-15 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 20 , 4870-7, (2010)] |
|
Acute and chronic effects of botulinum neurotoxin a on the m...
2014-08-01 [Muscle Nerve 50(2) , 206-15, (2014)] |
|
Orphan drugs. BioMarin Europe replies.
2010-01-01 [BMJ 341 , c7006, (2010)] |