| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
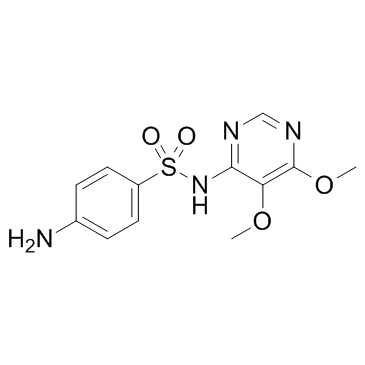 |
Sulfadoxine
CAS:2447-57-6 |
|
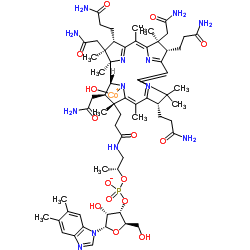 |
Hydroxocobalamin
CAS:13422-51-0 |
|
 |
Trimethoprim
CAS:738-70-5 |