| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
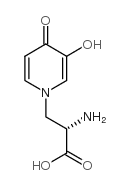 |
Mimosine
CAS:500-44-7 |
|
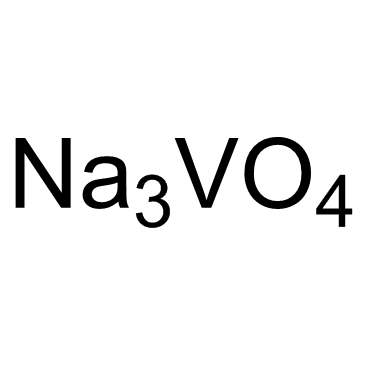 |
Sodium orthovanadate
CAS:13721-39-6 |
|
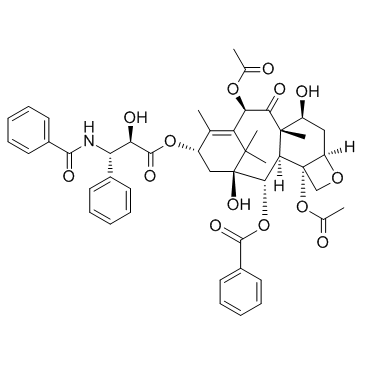 |
Paclitaxel
CAS:33069-62-4 |
|
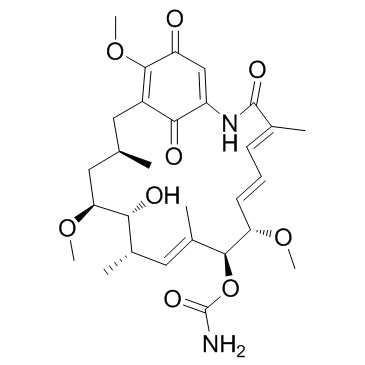 |
Geldanamycin
CAS:30562-34-6 |
|
 |
Nocodazole
CAS:31430-18-9 |