Condensation of beta-diester titanium enolates with carbonyl substrates: a combined DFT and experimental investigation.
Alessandro Marrone, Andrea Renzetti, Paolo De Maria, Stéphane Gérard, Janos Sapi, Antonella Fontana, Nazzareno Re
Index: Chemistry 15(43) , 11537-50, (2009)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The condensation of dialkyl beta-diesters with various aldehydes promoted by TiCl4 has been studied by DFT approaches and experimental methods, including NMR, IR and UV/Vis spectroscopy. Various possible reaction pathways have been investigated and their energy profiles evaluated to find out a plausible mechanism of the reaction. Theoretical results and experimental evidence point to a three-step mechanism: 1) Ti-induced formation of the enolate ion; 2) aldol reaction between the enolate ion and the aldehyde, both coordinated to titanium; and 3) intramolecular elimination that leads to a titanyl complex. The presented mechanistic hypothesis allows one to better understand the pivotal role of titanium(IV) in the reaction.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
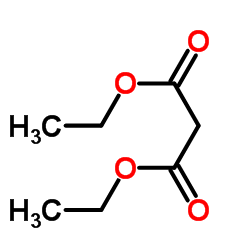 |
Diethyl malonate
CAS:105-53-3 |
C7H12O4 |
|
Design, synthesis and structure-activity relationship studie...
2014-12-01 [J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 29(6) , 846-67, (2014)] |
|
Identification of olfactory receptor neurons in Uraba lugens...
2015-07-01 [J. Insect Physiol. 78 , 33-46, (2015)] |
|
Ring expansion reactions of 4-amino-1,1-dioxo-[1,2,3,5]-thia...
2007-02-07 [Org. Biomol. Chem. 5(3) , 472-7, (2007)] |
|
Intramolecular Hydrogen Bonding and Linear Pentapyrrole Conf...
2014-08-01 [Monatsh. Chem 145(7) , 1117-1135, (2014)] |
|
Room-temperature copper-catalyzed alpha-arylation of malonat...
2007-08-16 [Org. Lett. 9(17) , 3469-72, (2007)] |