| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
RH 421
CAS:107610-19-5 |
|
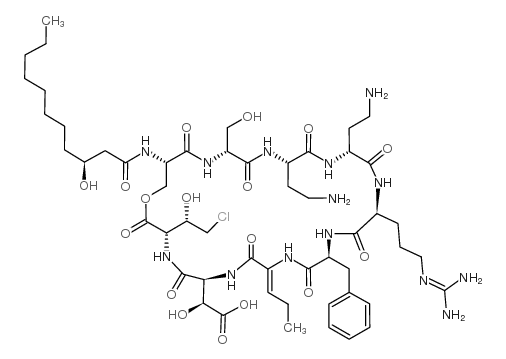 |
syringomycin E
CAS:124888-22-8 |
|
 |
6-Keto cholestanol
CAS:1175-06-0 |