| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
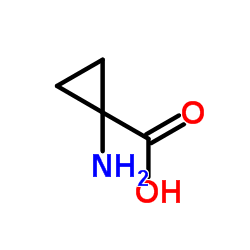 |
1-Aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid
CAS:22059-21-8 |
|
 |
1-Amino-cyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid hydrochloride
CAS:68781-13-5 |
|
 |
Noratropine
CAS:16839-98-8 |