| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Sodium Fluoride
CAS:7681-49-4 |
|
 |
sodium dodecyl sulfate
CAS:151-21-3 |
|
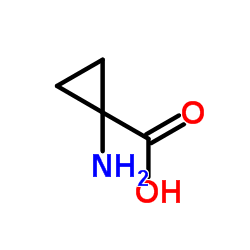 |
1-Aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid
CAS:22059-21-8 |
|
 |
HEPES
CAS:7365-45-9 |
|
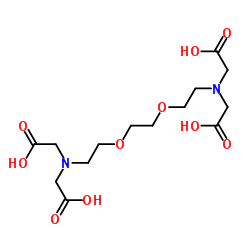 |
EGTA
CAS:67-42-5 |
|
 |
Glycerol
CAS:56-81-5 |
|
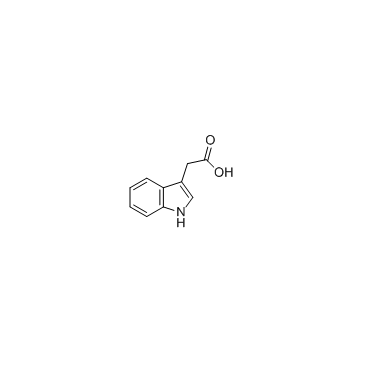 |
3-Indoleacetic acid
CAS:87-51-4 |
|
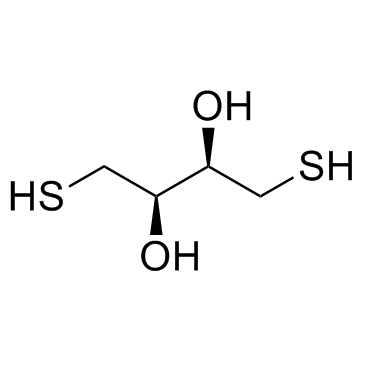 |
DL-Dithiothreitol
CAS:3483-12-3 |
|
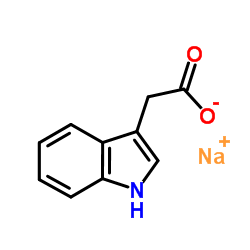 |
Sodium 1H-indol-3-ylacetate
CAS:6505-45-9 |
|
 |
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
CAS:60-00-4 |