| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
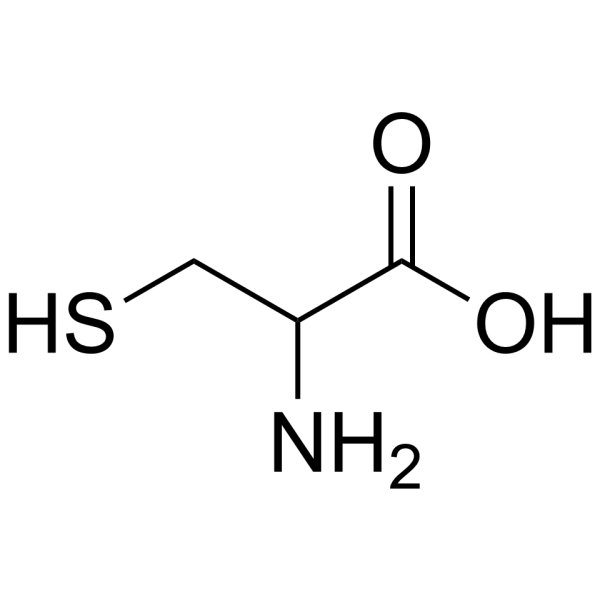 |
DL-CYSTEINE (1-13C)
CAS:3374-22-9 |
|
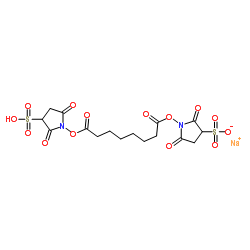 |
BS3 Crosslinker
CAS:82436-77-9 |
|
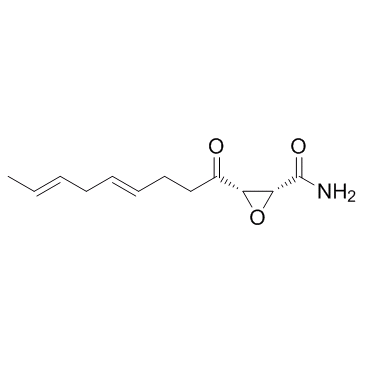 |
Cerulenin
CAS:17397-89-6 |