| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
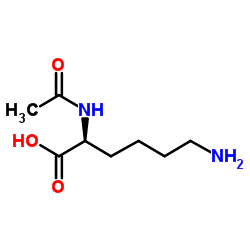 |
AC-Lys-OH
CAS:1946-82-3 |
|
 |
acetic acid
CAS:64-19-7 |
|
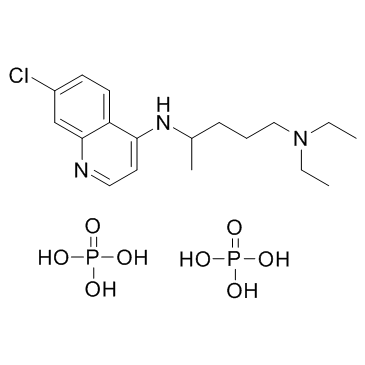 |
Chloroquine diphosphate
CAS:50-63-5 |
|
 |
tlck
CAS:4272-74-6 |
|
 |
Vorinostat(SAHA)
CAS:149647-78-9 |
|
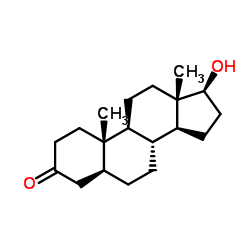 |
Stanolone
CAS:521-18-6 |
|
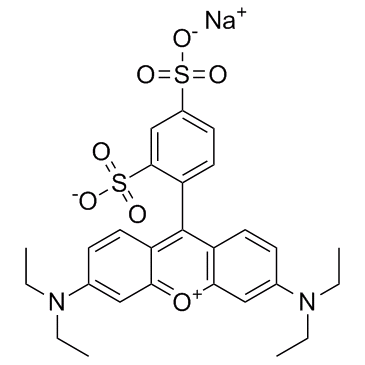 |
Acid Red 52
CAS:3520-42-1 |
|
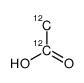 |
acetic acid
CAS:1173022-32-6 |