Purification and characterization of four monofluorescein cobra alpha-toxin derivatives.
D A Johnson, R Cushman
Index: J. Biol. Chem. 263(6) , 2802-7, (1988)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
We labeled cobra-alpha-toxin (Naja naja siamensis 3) with near stoichiometric quantities of fluorescein isothiocyanate. To reduce labeling of the hyperreactive N epsilon-lysine 23, the alpha-toxin was modified reversibly with citraconic anhydride before fluorescein labeling. The citraconic anhydride was later removed with strong acid, and four of the six possible monofluorescein alpha-toxin derivatives were isolated by isoelectric focusing on an immobilized pH gradient. Thermolysin digestion and subsequent high pressure liquid chromatography of the peptides yielded one dominant fluorescent peak from three of the isolated monofluorescein derivatives. Sequence analyses of these three fluorescent peaks indicated monofluorescein labeling at Lys-69, Lys-35, and Lys-49. Since one derivative (not identified by sequence analysis) displayed essentially identical chromatographic, spectroscopic, and binding properties as our previously identified monofluorescein-Lys-23 toxin (Johnson, D. A., and Taylor, P. (1982) J. Biol. Chem. 257, 5632-5636), we identified the site of labeling of this fourth derivative to be Lys-23. While only small differences were observed in the extinction maxima and molar extinction coefficients, the quantum yields of the isolated derivatives varied markedly and ranged between 0.18 and 0.41. Binding of monofluorescein-Lys-69, -Lys-35, -Lys-49, and -Lys-23 derivatives to the membrane-associated acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica was associated with -39, -26, -9, and +96% changes in fluorescence emission intensity, respectively. Based on analyses of the kinetics of fluorescence changes associated with receptor binding, the association and dissociation rate constants were measured. Relative to native cobra alpha-toxin, monofluorescein conjugation reduced the bimolecular association rate constants for binding to the receptor 13-33-fold. The dissociation rate binding rate constants were less affected and were reduced 0-5-fold.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
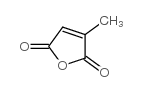 |
Citraconic anhydride
CAS:616-02-4 |
C5H4O3 |
|
MALDI imaging mass spectrometry profiling of N-glycans in fo...
2014-01-01 [PLoS ONE 9(9) , e106255, (2014)] |
|
Polymeric micelles with citraconic amide as pH-sensitive bon...
2014-08-25 [Int. J. Pharm. 471(1-2) , 28-36, (2014)] |
|
Pre-cultivation of adipose tissue-derived microvascular frag...
2015-01-01 [Eur. Cell. Mater. 29 , 190-200; discussion 200-1, (2015)] |
|
Experimental colitis in SIV-uninfected rhesus macaques recap...
2015-01-01 [Nat. Commun. 6 , 8020, (2015)] |
|
Dual-targeting and pH/redox-responsive multi-layered nanocom...
2015-08-01 [Biomaterials 60 , 42-52, (2015)] |