| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
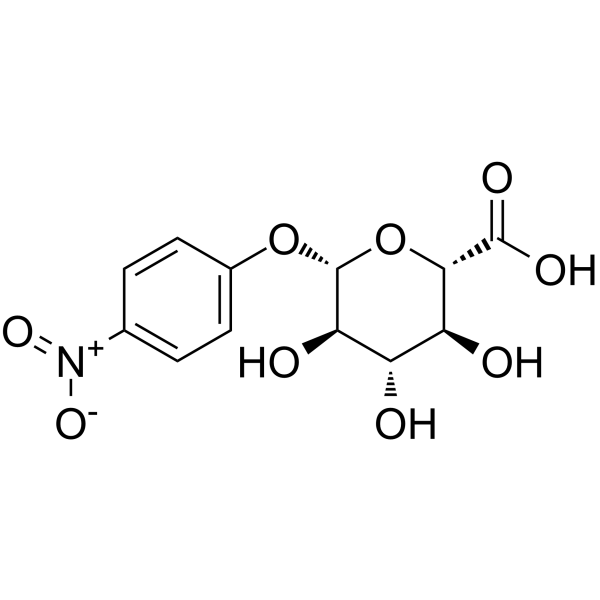 |
4-Nitrophenyl β-D-glucopyranosiduronic acid
CAS:10344-94-2 |
|
 |
ethyl acetate
CAS:141-78-6 |
|
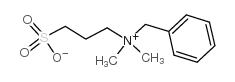 |
ndsb-256
CAS:81239-45-4 |
|
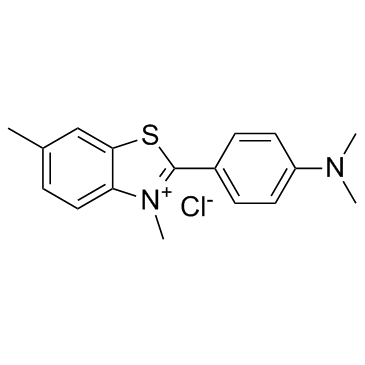 |
Thioflavine T
CAS:2390-54-7 |
|
 |
β-Amyloid-42
CAS:107761-42-2 |