[Fluorescence investigation on interaction between artemisinin (qinghaosu) and hemin and its analytical application].
Li-Hua Chen, Hong Yin, Zhao-Xia Yang, Ke-Mei Zhang, Liu-Zhan Liu, Han-Xi Shen
Index: Guang Pu Xue Yu Guang Pu Fen Xi 26(9) , 1640-3, (2006)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Hemin-catalytic decomposition of artemisinin (qinghaosu, QHS) was studied using pyronine B (PB) as an indicator. The interaction between hemin and QHS was an enzyme-substrate model, and the action sites were the endoperoxide moiety of QHS and the central metal ion of enzyme respectively. The kinetic catalytic constant depends upon enzyme and substrate concentrations, and the Michaelis-Menten parameters Km, Vmax and Kcat was 8.4 x 10(-5) mol x L(-1), 7.4 x 10(-6) mol x L(-1) s(-1) and 50.23 s(-1) respectively. The catalytic activity of hemin was inhibited in the presence of deactivated agents and at high temperature. Under optimal conditions, the change in fluorescence intensity (Fo-F) of pyronine B was proportional to the QHS concentration from 0.0 to 1.27 x 10(-6) mol x L(-1), and the detection limit (3sigma) was as low as 2.3 x 10(-8) mol x L(-1). The proposed method was applied to detect the concentration of QHS in the media of plasma and urine.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
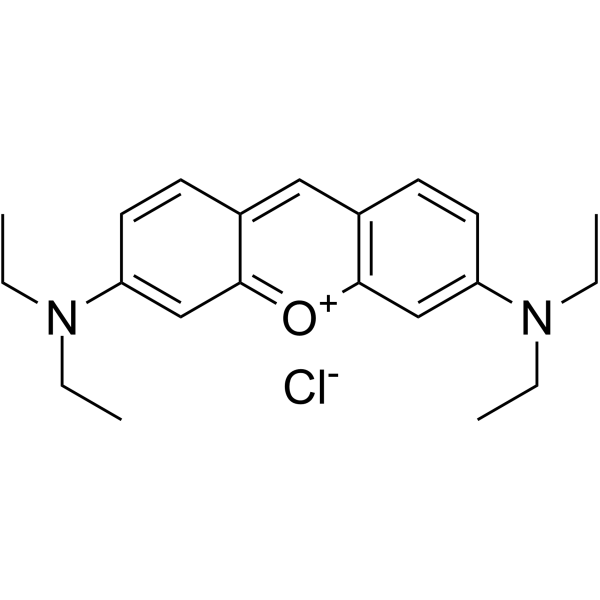 |
PYRONINE B
CAS:2150-48-3 |
C21H27ClN2O |
|
Analysis and testing of biological stains--the Biological St...
2002-01-01 [Biotech. Histochem. 77(5&6) , 237-275, (2002)] |
|
Nuclear dyes and cytoplasmic staining.
1997-12-01 [Cytometry 29(4) , 375-6, (1997)] |
|
Mouse hematopoietic stem cell identification and analysis.
2009-01-01 [Cytometry. A 75(1) , 14-24, (2009)] |
|
Nucleic acid dyes for detection of apoptosis in live cells.
1995-11-01 [Cytometry 21(3) , 265-74, (1995)] |
|
Nonaqueous catalytic fluorometric trace determination of van...
2001-09-15 [Anal. Chem. 73(18) , 4428-33, (2001)] |