| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
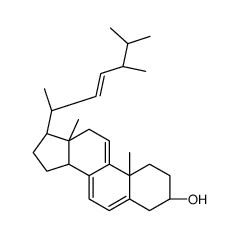 |
Dehydroergosterol
CAS:516-85-8 |
|
 |
L-Ascorbyl 6-palmitate
CAS:137-66-6 |