| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Sorbic acid
CAS:110-44-1 |
|
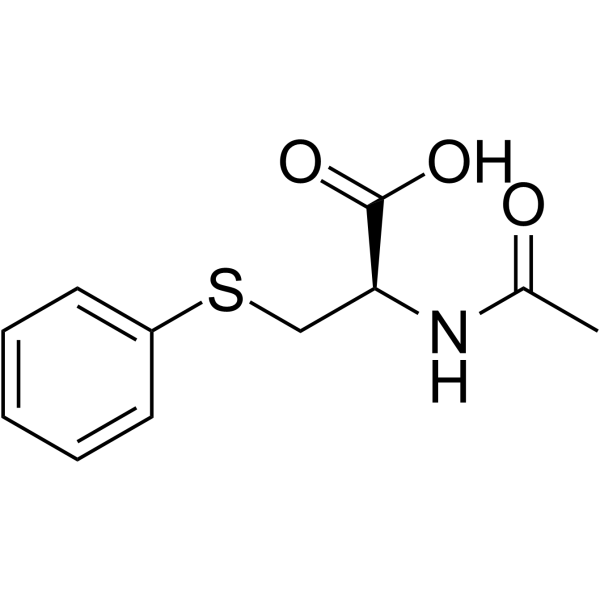 |
S-Phenylmercapturic Acid
CAS:4775-80-8 |
|
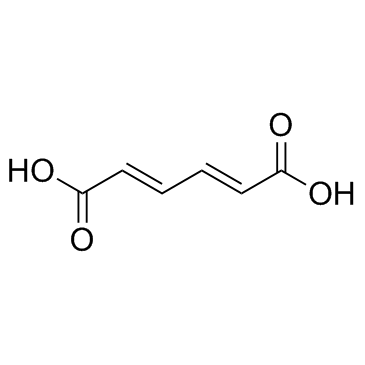 |
trans,trans-Muconic Acid
CAS:3588-17-8 |