| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
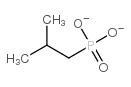 |
Isopropyl methylphosphonic acid
CAS:1832-54-8 |
|
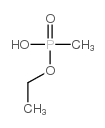 |
ETHYL METHYLPHOSPHONIC ACID
CAS:1832-53-7 |
|
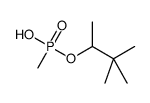 |
pinacolyl methylphosphonate
CAS:616-52-4 |