Synergistic antibacterial activity between L-norvalyl-L-1-aminoethylphosphonic acid and nocardicin A.
P Angehrn, M J Hall, W J Lloyd, D Westmacott
Index: Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 25(5) , 607-11, (1984)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The phosphonopeptide L- norvalyl -L-1- aminoethylphosphonic acid [ Nva -Ala(P)] has been studied in combination with 12 beta-lactam antibiotics for activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Nocardicin A was found to give the most potent synergistic combination with Nva -Ala(P). This interaction was widely observed in clinical isolates of P. aeruginosa in vitro and in a mouse septicemia model. Synergy was also observed in vitro and in vivo in several other species, including Proteus mirabilis, indole-positive Proteus spp., and Serratia marcescens. The interaction between Nva -Ala(P) and nocardicin A involved a strongly bacteriolytic mechanism. In addition, the individual components were complementary to one another in their action against organisms not showing synergy. These properties resulted in a broad spectrum of activity of the combination Nva -Ala(P) plus nocardicin A when used to treat experimental gram-negative bacterial infections.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
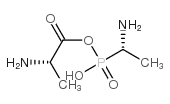 |
Alafosfalin
CAS:60668-24-8 |
C5H13N2O4P |
|
In vitro potentiation of cephalosporins by alafosfalin again...
1982-05-01 [Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 21(5) , 706-10, (1982)] |
|
Alafosfalin as a selective agent for isolation of salmonella...
2002-11-01 [J. Clin. Microbiol. 40(11) , 3913-6, (2002)] |
|
In vitro evaluation of alaphosphin (Ro 03-7008) against Serr...
1980-01-01 [Chemotherapy 26(2) , 103-10, (1980)] |
|
Alafosfalin, a new synthetic antibacterial compound.
1981-02-01 [Naturwissenschaften 68(2) , 90, (1981)] |
|
Recent developments in the field of phosphonic acid antibiot...
1984-10-01 [J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 14(4) , 309-11, (1984)] |