The genotoxicity of N4-aminocytidine in the Drosophila wing spot test.
T Negishi, K Negishi, H Ryo, S Kondo, H Hayatsu
Index: Mutagenesis 3(1) , 11-3, (1988)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The nucleoside analogue N4-aminocytidine is known to induce mutations in bacteria, and was shown to induce somatic mutations in Drosophila melanogaster after larval administration. The assay system employed was a wing-hair mutation spot test developed by Würgler and co-workers. The potency of N4-aminocytidine to induce somatic mutation is comparable to those of several food-pyrolysate mutagens previously reported. The occurrence of twin spots, i.e. two types of recessive mutant-hair clones in adjacent positions, suggests that N4-aminocytidine induces somatic recombination in Drosophila. Another feature of the mutagenicity of N4-aminocytidine is that both the acute and the chronic larval feedings gave rise to mutant hair formation of similar patterns with respect to the spot-size distributions: small single spots were formed predominantly and the larger the spot-size, the lower their frequency.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
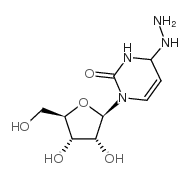 |
n4-aminocytidine
CAS:57294-74-3 |
C9H16N4O5 |
|
Genotoxic properties of representatives of alkylindazoles an...
2015-06-01 [Food Chem. Toxicol. 80 , 130-6, (2015)] |
|
Mutagenic nucleoside analog N4-aminocytidine: metabolism, in...
1988-11-01 [J. Bacteriol. 170(11) , 5257-62, (1988)] |
|
An improved synthesis of N4-aminocytidine.
1987-09-01 [Chem. Pharm. Bull. 35(9) , 3884-7, (1987)] |
|
[Molecular mechanism of N4-aminocytidine mutagenesis].
1990-05-01 [Yakugaku Zasshi 110(5) , 293-303, (1990)] |
|
Mutagenesis by N4-aminocytidine: induction of AT to GC trans...
1985-12-03 [Biochemistry 24 , 7273, (1985)] |