Differentiating amoebic ulcero-haemorrhagic recto-colitis from idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease: still a diagnostic dilemma.
T M Ibrahim, N Iheonunekwu, V Gill, H Vantapool
Index: West Indian Med. J. 54(3) , 210-2, (2005)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The colon responds monomorphically to a variety of insults thus making it difficult to differentiate invasive amoebic colitis and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). The authors present a case with chronic dysentery, haematochezia, anaemia and hypoproteinaemia. The endoscopic findings were suggestive of IBD. The stool examination was negative for trophozoites or cysts of parasites. The recto-colonic biopsy specimens showed mucosal inflammation with exudates containing amoebic trophozoites. The patient was successfully treated with metronidazole and iodoquinol. He recovered within two weeks and repeat colonoscopy four weeks after the treatment showed a normal rectum and colon. Clinicians should have a high level of suspicion for amoebic colitis in cases of colitis especially in regions where amoebiasis is still present. Efforts should be made to find the amoebic trophozoites in multiple stool and colonic biopsy specimens.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
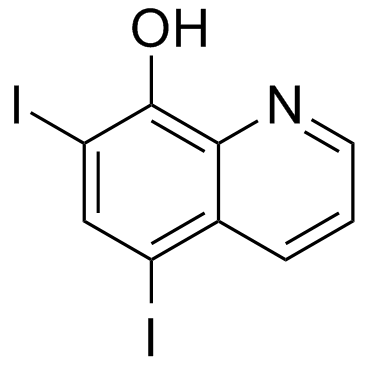 |
Diiodohydroxyquinoline
CAS:83-73-8 |
C9H5I2NO |
|
Effects of oral administration of zinc and diiodohydroxyquin...
1995-01-01 [Nephron 69(2) , 147-50, (1995)] |
|
Chromatographic methods for simultaneous determination of di...
2013-09-01 [Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 26(5) , 865-71, (2013)] |
|
LC of pharmaceutically important halogenated 8-hydroxyquinol...
2002-02-01 [J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 27(5) , 813-20, (2002)] |
|
Relapse of intestinal and hepatic amebiasis after treatment.
2011-03-01 [Dig. Dis. Sci. 56(3) , 677-80, (2011)] |
|
Pleural empyema secondary to rupture of amoebic liver absces...
2012-01-01 [Intern. Med. 51(5) , 471-4, (2012)] |