| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
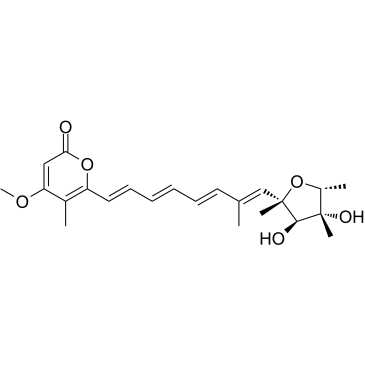 |
(-)-Citreoviridin
CAS:25425-12-1 |
|
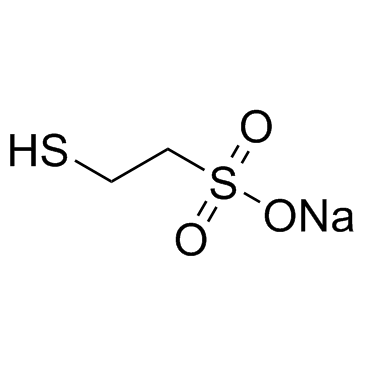 |
MESNA
CAS:19767-45-4 |
|
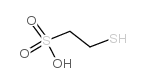 |
2-Mercaptoethanesulfonic acid
CAS:3375-50-6 |