| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
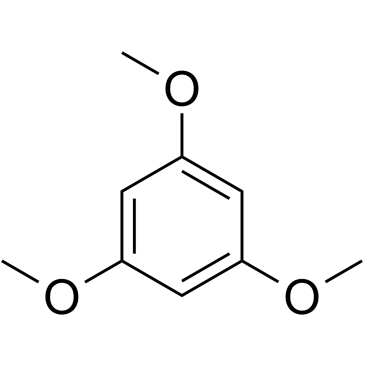 |
1,3,5-Trimethoxybenzene
CAS:621-23-8 |
|
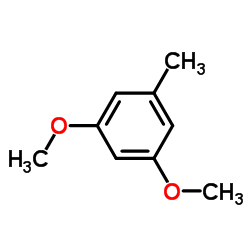 |
1,3-Dimethoxy-5-methylbenzene
CAS:4179-19-5 |
|
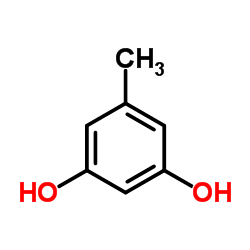 |
Orcinol
CAS:504-15-4 |