| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
DISIALOGANGLIOSIDE GD1B 2NA
CAS:19553-76-5 |
|
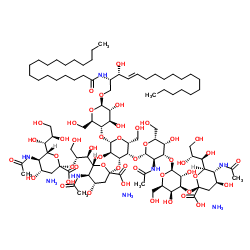 |
Ganglioside GT1b Mixture (bovine) (ammonium salt)
CAS:59247-13-1 |
|
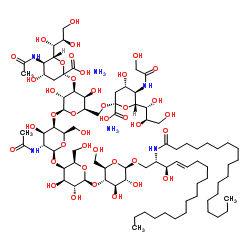 |
ganglioside gd1a disodium salt
CAS:12707-58-3 |