Two-dimensional NMR spectroscopy of siomycin A. Proton--carbon-13 chemical shift correlation.
N J Clayden, F Inagaki, R J Williams, G A Morris, K Tori, K Tokura, T Miyazawa
Index: Eur. J. Biochem. 123(1) , 127-31, (1982)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
A trial application of a recent two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance experiment to the polypeptide antibiotic siomycin A is described. Proton--carbon-13 chemical shift correlation measures the proton and carbon-13 chemical shift for each directly bonded CH group in a molecule, in a single experiment. The resultant map of correlated chemical shifts enables the carbon-13 spectrum to be assigned directly from the known proton shifts, and allows individual proton signals to be identified without problems of overlap. The signal-to-noise ratio available from such techniques should enable their application to aqueous protein solutions using currently available high-field spectrometers.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
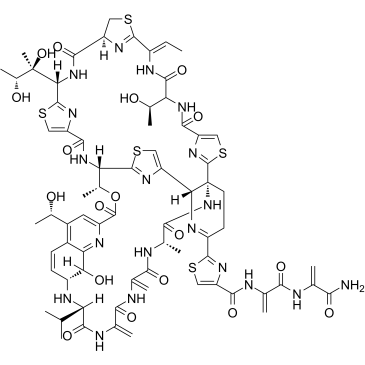 |
Siomycin A
CAS:12656-09-6 |
C71H81N19O18S5 |
|
A novel mode of FoxM1 regulation: positive auto-regulatory l...
2009-06-15 [Cell Cycle 8(12) , 1966-7, (2009)] |
|
Thiazole antibiotics target FoxM1 and induce apoptosis in hu...
2009-01-01 [PLoS ONE 4(5) , e5592, (2009)] |
|
The maternal embryonic leucine zipper kinase (MELK) is upreg...
2013-02-01 [J. Mol. Med. 91(2) , 237-48, (2013)] |
|
FOXM1: the Achilles' heel of cancer?
2008-02-01 [Nat. Rev. Cancer 8(3) , c1; author reply c2, (2008)] |
|
Future roles for FoxM1 inhibitors in cancer treatments.
2007-02-01 [Future Oncol. 3(1) , 1-3, (2007)] |