Evaluation of the teratogenic potential of the oxidative dye N-phenyl-para-phenylenediamine.
J C Picciano, R W Schnetzinger, W E Morris, B A Wolf, D E Rodwell
Index: Drug Chem. Toxicol. 7(2) , 167-76, (1984)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The oxidative dye N-phenyl-para-phenylenediamine was evaluated for teratogenic potential. The dye was administered by gavage to pregnant Sprague-Dawley rats at dose levels of 50, 100, and 200 mg/kg on gestation days six through fifteen. No signs of toxicity were observed during the treatment period. A significant reduction in mean maternal weight gain was noted during treatment at the high dose level of 200 mg/kg. The test material did not produce embryotoxic nor fetal toxic effects at dose levels utilized. Evaluation of fetal external, visceral, and skeletal anomalies revealed no statistically significant differences between dye treated and control groups. Oral exposure of dams to the positive control, Vitamin A, resulted in a significant increase in the number of litters with fetuses having external, visceral, and skeletal anomalies.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
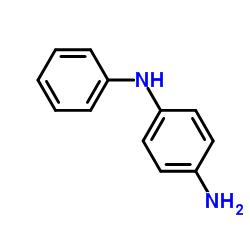 |
4-Aminodiphenylamine
CAS:101-54-2 |
C12H12N2 |
|
Preventive effect of phytic acid on lysosomal hydrolases in ...
2015-02-01 [Toxicol. Mech. Methods 25(2) , 150-4, (2015)] |
|
Rational design of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase inhibitors.
2010-02-11 [J. Med. Chem. 53 , 1172-89, (2010)] |
|
In vitro studies on the biotransformation of metanil yellow.
1982-02-01 [Environ. Res. 27(1) , 185-9, (1982)] |
|
Bulk synthesis, optimization, and characterization of highly...
2012-11-15 [J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 386(1) , 148-57, (2012)] |
|
p-Anilinoaniline enhancement of dioxin-induced CYP1A1 transc...
2012-05-01 [Drug Metab. Dispos. 40(5) , 1032-40, (2012)] |