pH-dependent inhibition of mushroom tyrosinase by N-substituted N-nitrosohydroxylamines.
Mitsuhiro Shiino, Yumi Watanabe, Kazuo Umezawa
Index: J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 23(1) , 16-20, (2008)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Several synthetic N-substituted N-nitrosohydroxylamines were found to inhibit mushroom tyrosinase in a pH-dependent manner regardless of the N-substituent. The inhibitory activity, or pI(50) ( - log [IC(50), M]) value, linearly decreased as the pH of the media increased. The inhibitory activities of tested N-substituted N-nitrosohydroxylamines at pH 6.8 and 5.8 were found to be almost 10 times and 100 times greater than at pH 7.8, respectively. The types of inhibition were different at pH 6.8 and 5.8. These results suggest that the inhibitory effect of N-substituted N-nitrosohydroxylamines is caused by the non-ionized form of the inhibitor. Furthermore, the mechanism of inhibition depends on the interaction between the inhibitor and the active site of tyrosinase at different pH values.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
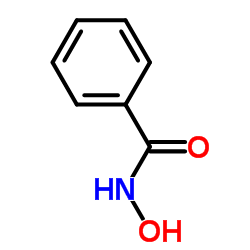 |
Benzohydroxamic acid
CAS:495-18-1 |
C7H7NO2 |
|
Multi-target spectral moment QSAR versus ANN for antiparasit...
2010-03-15 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. 18 , 2225-31, (2010)] |
|
Intermediate analogue inhibitors of mandelate racemase: N-Hy...
2007-01-01 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 17 , 105-8, (2007)] |
|
Dephosphorylation reactions of mono-, di-, and triesters of ...
2012-12-07 [J. Org. Chem. 77(23) , 10907-13, (2012)] |
|
Optical spectra of lactoperoxidase as a function of solvent.
2005-12-06 [Biochemistry 44(48) , 15953-9, (2005)] |
|
Nanomolar inhibition of the enterobactin biosynthesis enzyme...
2006-07-15 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 16(14) , 3802-5, (2006)] |