LC-MS/MS method for the determination of the fungal pigment bikaverin in maize kernels as an indicator of ear rot.
M Busman, R A E Butchko, R H Proctor
Index: Food Addit. Contam. Part A. Chem. Anal. Control. Expo. Risk Assess. 29(11) , 1736-42, (2012)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Bikaverin is a polyketide-derived pigment produced by multiple species of the fungus Fusarium, some of which can cause ear and kernel rot of maize. A method was developed for the analysis of bikaverin by high-performance liquid chromatography (LC) coupled to electrospray ionisation tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS). The quantitative nature of the LC-MS/MS method was demonstrated over a range of concentrations of bikaverin in maize. For spike-recovery experiments utilising maize spiked with bikaverin to a level 5 µg g⁻¹ of maize, the measured recovery (%) was 70.6 ± 10.4. Based on the utilised method, the limit of detection (based on a signal-to-noise ratio (S/N) > 3) was better than 0.5 µg g⁻¹ from bikaverin spiked into uncontaminated ground maize. Further, the limit of quantitation (LOQ) was 3 µg g⁻¹ (based on S/N > 10) from bikaverin spiked into ground maize. The method was applied to assess contamination of maize with bikaverin following inoculation of developing maize ears with Fusarium verticillioides under agricultural field conditions.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
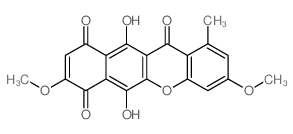 |
Bikaverin
CAS:33390-21-5 |
C20H14O8 |
|
Bikaverin and fusaric acid from Fusarium oxysporum show anti...
2008-03-01 [J. Appl. Microbiol. 104(3) , 692-8, (2008)] |
|
United States Department of Agriculture-Agricultural Researc...
2003-01-01 [Pest Manag. Sci. 59(6-7) , 736-47, (2003)] |
|
GAC1, a gene encoding a putative GTPase-activating protein, ...
2008-01-01 [Mycologia 100(5) , 701-9, (2008)] |
|
Stimulation of bikaverin production by sucrose and by salt s...
2010-02-01 [Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 85(6) , 1991-2000, (2010)] |
|
FUMandBIKgene expression contribute to describe fumonisin an...
2012-11-15 [Int. J. Food Microbiol. 160(2) , 94-8, (2012)] |