| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
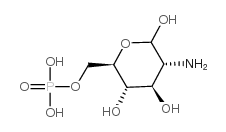 |
D-Glucosamine 6-phosphate
CAS:3616-42-0 |
|
 |
d-glucosamine 6-phosphate sodium salt
CAS:70442-23-8 |