Update on atrial fibrillation: part II.
Irina Savelieva, John Camm
Index: Clin. Cardiol. 31(3) , 102-8, (2008)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Antiarrhythmic drugs are an essential tool in the management of atrial fibrillation (AF). Although we are already on the threshold of a large expansion in the use of ablation therapies, these will not, however, be appropriate for all patients, and pharmacological therapies will continue to have an important place in the management of atrial fibrillation. The plethora of antiarrhythmic drugs currently available for the treatment of atrial fibrillation is a reflection that none is wholly satisfactory, each having limited efficacy combined with poor safety and tolerability. Improved class III antiarrhythmic drugs, such as dronedarone, new classes of antiarrhythmic agents, such as atrial repolarization delaying agents, and upstream therapies dealing with substrate, represent potential sources of new pharmacological therapies.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
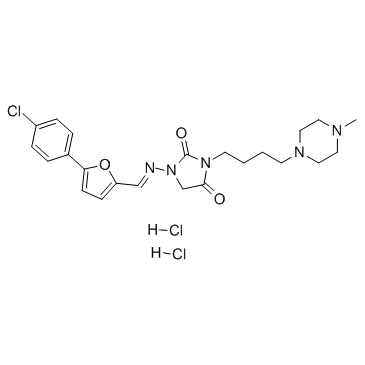 |
Azimilide (Dihydrochloride)
CAS:149888-94-8 |
C23H30Cl3N5O3 |
|
Azimilide dihydrochloride: a new class III anti-arrhythmic a...
2000-11-01 [Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 9(11) , 2705-15, (2000)] |
|
Electrophysiological and antiarrhythmic effects of the novel...
2006-07-01 [Europace 8(7) , 549-57, (2006)] |
|
Azimilide for the treatment of atrial fibrillation, atrial f...
2008-02-01 [J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 19(2) , 172-7, (2008)] |
|
Role of drug therapy for sustained ventricular tachyarrhythm...
2008-08-01 [Cardiol. Clin. 26(3) , 405-18, vi, (2008)] |
|
Effects of azimilide on the muscarinic acetylcholine recepto...
2007-11-01 [J. Pharmacol. Sci. 105(3) , 229-39, (2007)] |