Pharmacology of the pyrazolo-type compounds: agonist, antagonist and inverse agonist actions.
D A Bennett
Index: Physiol. Behav. 41(3) , 241-5, (1987)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Five compounds that bind to the benzodiazepine (BZ) receptor, but show different pharmacological characteristics from the classical BZs, are profiled. CGS 8216 is a BZ antagonist/inverse agonist that reverses the effects of diazepam and also acts as a proconvulsant. CGS 9895 is also a potent BZ antagonist. In addition, this compound shows an anxiolytic profile. CGS 9896, CGS 17867A and CGS 20625 are BZ agonists (i.e., anxiolytics and anticonvulsants) which produce varying magnitudes of antagonist effect. All of these compounds are unique from the classical BZs in that each has a reduced propensity to produce the sedative and/or muscle relaxant effects characteristically associated with BZs.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
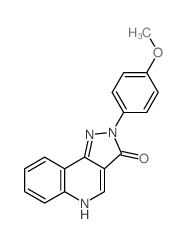 |
CGS-9895
CAS:77779-50-1 |
C17H13N3O2 |
|
Benzodiazepine receptor ligands modulate ethanol drinking in...
1994-09-22 [Eur. J. Pharmacol. 263(1-2) , 141-7, (1994)] |
|
Comparison of a new class of pyrrole containing benzodiazepi...
1994-01-01 [Med. Chem. Res. 4(5) , 307-14, (1994)] |
|
Benzodiazepine-induced hyperphagia: stereospecificity and an...
1986-01-01 [Psychopharmacology 89(4) , 462-6, (1986)] |
|
Differential diazepam-antagonist effects of the benzodiazepi...
1985-12-01 [J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 235(3) , 589-95, (1985)] |
|
Antagonism of the discriminative effects of diazepam by pyra...
1983-08-19 [Eur. J. Pharmacol. 92(1-2) , 155-7, (1983)] |