Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) response to a zinc fertilizer applied as zinc lignosulfonate adhered to a NPK fertilizer.
Diego Martín-Ortiz, Lourdes Hernández-Apaolaza, Agustín Gárate
Index: J. Agric. Food Chem. 58(13) , 7886-92, (2010)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The efficacy as Zn fertilizers for wheat of zinc lignosulfonate (ZnLS) products adhered to NPK was evaluated by three plant experimental designs. In the first and second assays, wheat plants were grown under controlled conditions with perlite and a calcareous soil as substrate, respectively. Shoot dry matter and Zn concentration showed that NPK + ZnLS was a better Zn source for wheat than NPK + ZnSO(4) under our experimental conditions. A third experiment was conducted under field conditions on a calcareous soil with a low Zn level. Wheat samples were taken at five growth stages of the crop. Although at early stages NPK + ZnLS was the most efficient source of Zn, at harvest no significant differences among treatments were found. Despite that, NPK + ZnLS showed evidence of being a useful Zn source for wheat crop under calcareous conditions.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
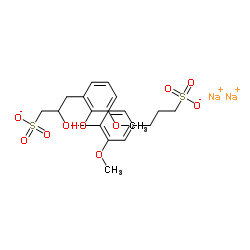 |
Sodium lignosulfonate
CAS:8061-51-6 |
C20H24Na2O10S2 |
|
The inhibitory effect of the various seed coating substances...
2009-08-15 [Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 12(16) , 1102-10, (2009)] |
|
Preparation, processing and properties of lignosulfonate-fla...
2013-03-01 [Carbohydr. Polym. 93(1) , 300-6, (2013)] |
|
Fabrication, characterization and application of nitrogen-co...
2013-01-01 [Bioresour. Technol. 127 , 66-71, (2013)] |
|
Oxygen-scavenging coatings and films based on lignosulfonate...
2012-09-15 [J. Biotechnol. 161(1) , 14-8, (2012)] |
|
Effects of corn grain particle size and treated soybean meal...
2011-08-01 [Meat Science 88(4) , 750-4, (2011)] |