Oxygen-scavenging coatings and films based on lignosulfonates and laccase.
Kristin Johansson, Sandra Winestrand, Caisa Johansson, Lars Järnström, Leif J Jönsson
Index: J. Biotechnol. 161(1) , 14-8, (2012)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Laccase and lignosulfonates were included in coating colors and embedded in latex-based or starch-based films and coatings on foil or board. After 6 days at 23 °C and 100% relative humidity, the oxygen content in airtight chambers decreased from 1.0% (synthetic gas consisting of 99% N(2) and 1% O(2)) to 0.3% in the presence of board coated with lignosulfonate and laccase, while the oxygen content remained unchanged in control experiments without enzyme. The water stability of lignosulfonate-containing latex-based coatings and starch-based films was improved after laccase-catalyzed oxidation of lignosulfonates, which indicates polymerization to products with lower solubility in water. Furthermore, the E' modulus of starch-based films increased with 30%, which indicates laccase-catalyzed polymerization of lignosulfonates resulting in increased stiffness of the film. The results suggest that laccases and lignosulfonates can be used as an oxygen-scavenging system in active packaging and that enzyme-catalyzed polymerization of lignosulfonates contributes to improved water stability and mechanical properties.Copyright © 2012 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
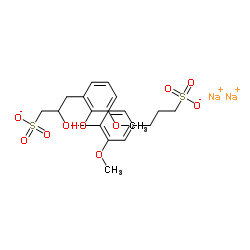 |
Sodium lignosulfonate
CAS:8061-51-6 |
C20H24Na2O10S2 |
|
The inhibitory effect of the various seed coating substances...
2009-08-15 [Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 12(16) , 1102-10, (2009)] |
|
Preparation, processing and properties of lignosulfonate-fla...
2013-03-01 [Carbohydr. Polym. 93(1) , 300-6, (2013)] |
|
Fabrication, characterization and application of nitrogen-co...
2013-01-01 [Bioresour. Technol. 127 , 66-71, (2013)] |
|
Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) response to a zinc fertilizer a...
2010-07-14 [J. Agric. Food Chem. 58(13) , 7886-92, (2010)] |
|
Effects of corn grain particle size and treated soybean meal...
2011-08-01 [Meat Science 88(4) , 750-4, (2011)] |