Experimental study of clinafloxacin alone and in combination in the treatment of ciprofloxacin-susceptible and -resistant pneumococcal meningitis.
A Domenech, C Cabellos, S Ribes, F Tubau, P F Viladrich, J Liñares, F Gudiol
Index: Microb. Drug Resist. 9 Suppl 1 , S53-9, (2003)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The increasing incidence of ciprofloxacin resistance in Streptococcus pneumoniae may limit the efficacy of the new quinolones in difficult-to-treat infections such as meningitis. The aim of the present study was to determine the efficacy of clinafloxacin alone and in combination with teicoplanin and rifampin in the therapy of ciprofloxacin-susceptible and ciprofloxacin-resistant pneumococcal meningitis in rabbits. When used against a penicillin-resistant ciprofloxacin-susceptible strain (Clinafloxacin MIC 0.12 microg/ml), clinafloxacin at a dose of 20 mg/kg per day b.i.d. decreased bacterial concentration by -5.10 log cfu/ml at 24 hr. Combinations did not improve activity. The same clinafloxacin schedule against a penicillin- and ciprofloxacin-resistant strain (Clinafloxacin MIC 0.5 microg/ml) was totally ineffective. Our data suggest that a moderate decrease in quinolone susceptibility, as indicated by the detection of any degree of ciprofloxacin resistance, may render these antibiotics unsuitable for the management of pneumococcal meningitis.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
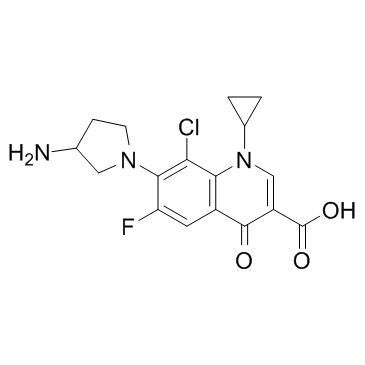 |
Clinafloxacin
CAS:105956-97-6 |
C17H17ClFN3O3 |
|
Pharmacokinetics of danofloxacin and N-desmethyldanofloxacin...
2015-04-01 [J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 38(2) , 123-9, (2015)] |
|
Accumulation of garenoxacin by Bacteroides fragilis compared...
2003-10-01 [J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 52(4) , 605-9, (2003)] |
|
Synthesis and antibacterial activity of novel pyrido[1,2,3-d...
2008-06-12 [J. Med. Chem. 51 , 3238-49, (2008)] |
|
In vitro activity of clinafloxacin in comparison with other ...
2002-02-01 [Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 42(2) , 123-8, (2002)] |
|
Photo-chemically induced DNA effects in the comet assay with...
2006-10-10 [Mutat. Res. 609(1) , 1-10, (2006)] |