A prospective, randomized, multicenter comparative study of clinafloxacin versus a ceftriaxone-based regimen in the treatment of hospitalized patients with community-acquired pneumonia.
W Petermann, J Alegre-Martin, I Odenholt, M J Phillips, P A Willcox, K Tack, U Trostmann, L Welling
Index: Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 33(11) , 832-7, (2001)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
In an open-label, phase 3, randomized, multicenter study, clinafloxacin (200 mg/d) was compared to ceftriaxone (2 g/d; with or without erythromycin) in 527 patients with acute community-acquired bacterial pneumonia (CAP). Primary efficacy parameters were clinical cure rate and microbiologic eradication rates (by pathogen and by patient) determined 5-9 d post-therapy (test of cure; TOC). Clinical cure rates at TOC for the 2 treatment groups were equivalent in the intention-to-treat (clinafloxacin 79.3, ceftriaxone 78.6%), clinically evaluable (clinafloxacin 88.1, ceftriaxone 85.0%), modified intention-to-treat (clinafloxacin 82.6, ceftriaxone 86.9%) and microbiologically evaluable populations (clinafloxacin 86.2, ceftriaxone 86.2%). Microbiologic eradication rates were similar in the 2 treatment groups. Both drugs were tolerated. Treatment of hospitalized CAP patients with clinafloxacin is a reasonable choice, especially when a resistant pathogen is anticipated.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
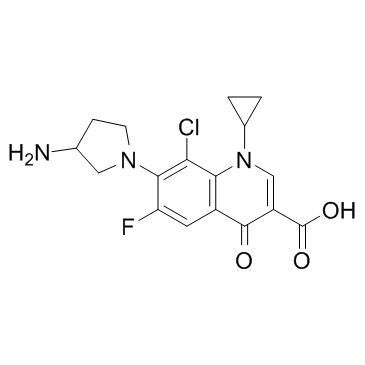 |
Clinafloxacin
CAS:105956-97-6 |
C17H17ClFN3O3 |
|
Pharmacokinetics of danofloxacin and N-desmethyldanofloxacin...
2015-04-01 [J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 38(2) , 123-9, (2015)] |
|
Accumulation of garenoxacin by Bacteroides fragilis compared...
2003-10-01 [J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 52(4) , 605-9, (2003)] |
|
Synthesis and antibacterial activity of novel pyrido[1,2,3-d...
2008-06-12 [J. Med. Chem. 51 , 3238-49, (2008)] |
|
In vitro activity of clinafloxacin in comparison with other ...
2002-02-01 [Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 42(2) , 123-8, (2002)] |
|
Photo-chemically induced DNA effects in the comet assay with...
2006-10-10 [Mutat. Res. 609(1) , 1-10, (2006)] |