2-Hydroxy-4-methoxybenzaldehyde: a potent tyrosinase inhibitor from African medicinal plants.
I Kubo, I Kinst-Hori
Index: Planta Med. 65(1) , 19-22, (1999)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
By bioassay-guided fractionation using mushroom tyrosinase (EC 1.14.18.1), 2-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzaldehyde was characterized as the principal tyrosinase inhibitor from three East African medicinal plants, the root of Mondia whitei (Hook) Skeels (Asclepiaceae), the root of Rhus vulgaris Meikle (Anacardiaceae), and the bark of Sclerocarya caffra Sond (Anacardiaceae). It inhibited the oxidation of L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (L-DOPA) by mushroom tyrosinase with an ID50 of 4.3 micrograms/ml (0.03 mM). The inhibition kinetics analyzed by a Lineweaver-Burk plot found this simple benzaldehyde derivative to be a mixed type inhibitor for this oxidation and affects on the enzyme in several ways. Based on finding this potent tyrosinase inhibitor, various related analogues were also tested in order to gain new insights into their inhibitory functions on a molecular basis.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
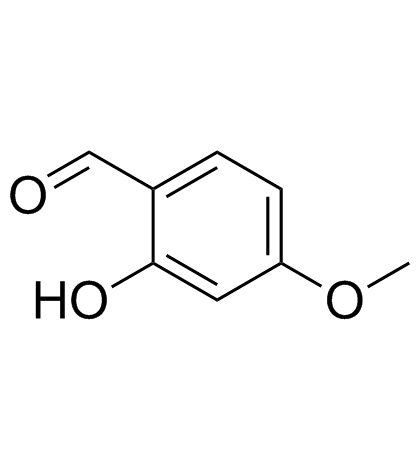 |
2-Hydroxy-4-methoxybenzaldehyde
CAS:673-22-3 |
C8H8O3 |
|
3D-QSAR and molecular docking studies of benzaldehyde thiose...
2007-03-01 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. 15 , 2006-15, (2007)] |
|
Flavoring extracts of Hemidesmus indicus roots and Vanilla p...
2013-09-01 [Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 68(3) , 247-53, (2013)] |
|
Inhibition of Cancer Cell Proliferation and Antiradical Effe...
2015-06-01 [Phytother Res. 29 , 857-63, (2015)] |
|
Shikimate pathway modulates the elicitor-stimulated accumula...
2012-07-01 [Plant Physiol. Biochem. 56 , 104-8, (2012)] |
|
Antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of the root bark es...
2010-08-01 [Molecules 15(8) , 5807-17, (2010)] |